Projects
We have a long history of developing solutions to difficult data questions through our research projects. The results of our research offer insights that can help patients and their doctors make more informed decisions.
CAPriCORNCAPriCORN is a patient-centered outcomes and research network.
CAPriCORN is a patient-centered outcomes and research network representing an ethnically and socioeconomically diverse population with significant disparities in access to and utilization of healthcare. Through its unique array of partners, including leading area medical institutions served by robust EHR systems and community partners engaged in health promotion and healthcare in the area, CAPriCORN will:
- Establish a network to share data
- Identify a cohort of over one million patients in the Chicago area
- Establish a sustainable platform for patient-centered outcomes research that engages clinicians, patients, and other stakeholders in carrying out meaningful research.
This project in designing the CAPriCORN network, scaling up knowledge of data linking and distributing query platform customization to centralize a data hub for Chicago area institutions.
Abel Kho serves as the PI of CAPriCORN central. Local site leadership for the Northwestern University site is Faculty Member Dr. Faraz Ahmad.
Learn more on the CAPriCORN website.
Collaborators: Alliance of Chicago, Center for Medical Technology Policy, Clinical Directors Network, Cook County Health and Hospital Systems, Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, Loyola University Medical Center, Medical Research Analytics and Informatics Alliance (MRAIA), NorthShore University Health System, Rand Corporation, Rush University Medical Center, Tufts Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute, University of Chicago Medicine, University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System, VA Healthcare, Vanderbilt University
Supporting Collaborators: AbbVie, BlueCross BlueShield of Illinois, CHITREC, Chicago Asthma Consortium, Chicago Department of Public Health — Healthy Chicago, Cook County, Columbia University STRIVE, Have A Heart for Sickle Cell Anemia Foundation, HealthCare Research Associates, Horizon Pharma, Illinois Association of Blood Banks, IBio Institute, Illinois Department of Public Health, Illinois Health and Hospital Association, Illinois Medical District Commission, PASTORS4PCOR, The Peggy Lillis Memorial Foundation, Respiratory Health Association, Sickle Cell Disease Association of Illinois, University of Chicago Medicine Comer Children’s Hospital, VA Information Resource Center, Vizient
CIRCL-ChicagoCommunity Intervention to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease in Chicago (CIRCL-Chicago)
Community Interventionot Reduce Cardiovascular Disease in Chicago (CIRCL-Chicago) is a federally funded research program to improve high blood pressure (hypertension) control in the Chicago South Side community. In Chicago, the prevalence of high blood pressure is higher among Black than white residents, and that gap is widening.
The CIRCL-Chicago study will evaluate the effectiveness of a community-driven adaptation of the Kaiser hypertension bundle, a collection of interventions and strategies designed to increase blood pressure control rates. The bundle includes a high blood pressure registry (i.e., list of patients), education on blood pressure measurement and treatment, feedback on blood pressure control rates, regular follow-up visits for blood pressure measurement, medication recommendations, and links to community resources.
For this study, Northwestern has partnered with faith-based organizations (FBOs) and community health centers (CHCs) in the South Side of Chicago. This team-based approach will increase coordinated care between clinic and community settings to improve hypertension control for Chicago’s South Side residents.
Co-Principal Investigators:
Abel Kho, MD, MS, FACMI
Paris Davis, PhD, MBA
JD Smith, PhD
Community Organization Collaborators:
Pastors4PCOR
Total Resource Community Development Organization
Clinical Partners:
Access Community Health Network (ACCESS)
Advocate Aurora Health
Academic Research Collaborators:
University of Chicago
University of Utah
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Funding:
This project is supported by a Disparities Elimination through Coordinated Interventions to Prevent and Control Heart and Lung Disease Risk award of the National Heart, Lung, And Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under Award Number U3HL154297.The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Contact:
Contact the CIRCL-Chicago team at circl-chicago@northwestern.edu with any questions, or if you're interested in participating in the research study.
Blood Pressure Information for Participants
Resources in English
- Blood pressure -- What do the numbers mean?: Understand blood pressure readings
- DASH Eating Plan: Learn about the DASH diet focus on fruits and vegetables, low fat milk products,
and whole grains - How to Manage Blood Pressure: Learn how to read blood pressure numbers and get tips for managing blood pressure.
- Sodium Shakedown: Read about why we should limit sodium intake and see sodium amounts in common foods
Recursos en español (Resources in Spanish)
- Aprenda a leer las etiquetas de los alimentos: How to read food labels (Spanish)
- La presión arterial alta y la dieta DASH: An overview of high blood pressure and the DASH diet (Spanish)
Community Resources for Help on the South Side of Chicago
Housing Assistance
- Total Resource Community Development Organization (a CIRCL-Chicago partner)
- City of Chicago Emergency Rental Assistance
- Illinois Housing Development Authority: Offers rent, mortgage, utility, and legal assistance
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
Food Assistance
- Total Resource Community Development Organization (a CIRCL-Chicago partner)
- Greater Chicago Food Depository
- Catholic Charities of Chicago: Offers a range of food assistance including SNAP enrollment, food pantries, and home delivered meals for seniors
- Chicago Department of Public Health Food Resources
Transportation Assistance
- Total Resource Community Development Organization (a CIRCL-Chicago partner)
- Regional Transportation Authority Free Transportation and Reduced Fares: Offers free and reduced fare permits for CTA, Metra, and Pace for eligible adults (senior, people with disabilities, and military)
Electric, Gas, Oil, or Water Utility Billing Assistance
- Total Resource Community Development Organization (a CIRCL-Chicago partner)
- City of Chicago Energy Billing Relief Program & LIHWAP: Water, sewer, and water-sewer utility billing assistance
- Community and Economic Development Association of Cook County (CEDA) Utility Bill Assistance: Offers assistance with gas, electric, and water utility bill payments, and furniture repair/replacement
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) utility assistance for Illinois
Resources for Safety or Violence:
- Total Resource Community Development Organization (a CIRCL-Chicago partner)
- Illinois Domestic Violence Hotline available at (877) 863-6338: Anonymous hotline open 24/7
- Metropolitan Family Services: Offers adult protective services, domestic violence clinical services, individual and family counseling, and legal aid services
Help with Barriers to Work
- Phalanx Family Services: Bridges the gap of financial barriers that may prevent individuals from being successful as they transition into work activity, training, and employment. Financial assistance available to help stabilize housing.
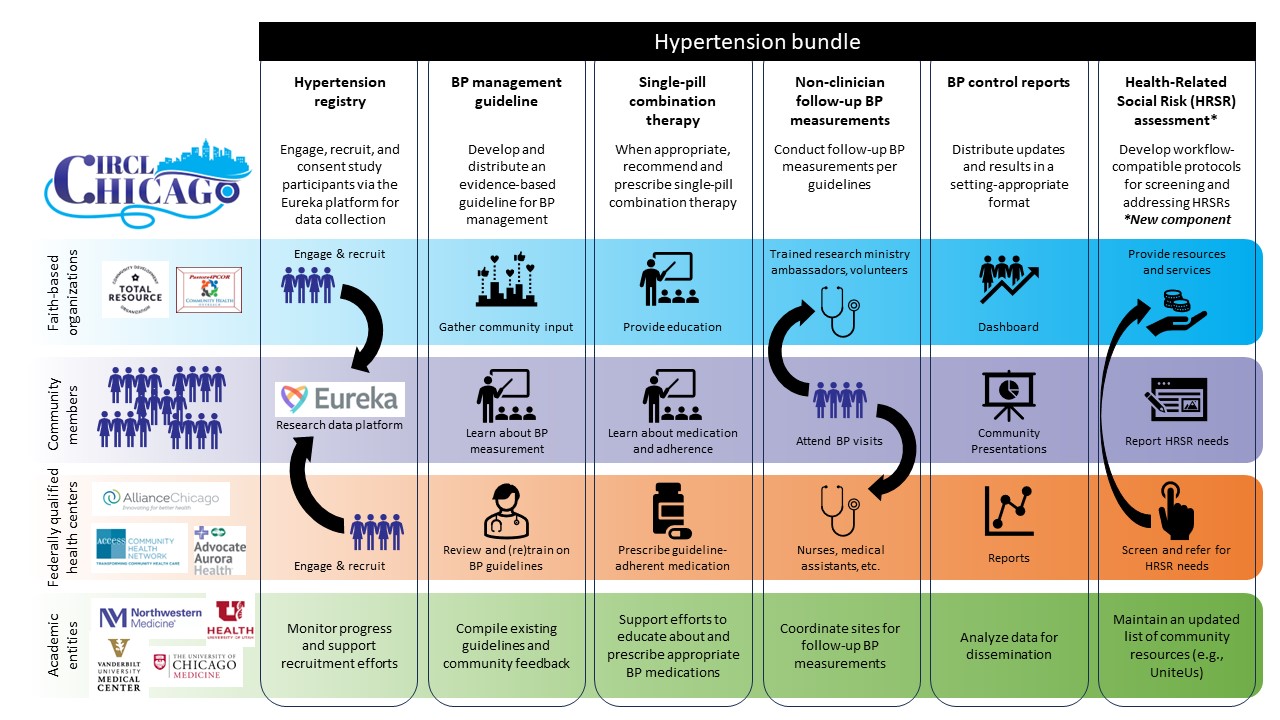
Blood Pressure Intervention (Kaiser Bundle)
The CIRCL-Chicago research study will evaluate the effectiveness of a community-driven adaptation of the Kaiser hypertension bundle. This figure illustrates how CIRCL-Chicago will implement the adaptation.
- Overview of Hypertension with Resources on Single-Pill Treatment: Explains how using the Kaiser Bundle can treat high blood pressure
Clinical Resources
- Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide: Based on the 2018 Kaiser Permanente National Blood Pressure (BP) Guidelines, the guide was developed to assist with screening and treatment of elevated BP in non-pregnant adults aged ≥ 18 years.
- BP Treatment Algorithm -- Patients with Stage 2 Hypertension Not on Medication: An ACCESS Community Health Network flow chart to aid in decision making around medication prescribing
- Cardiovascular Health Medication Adherence ACTION STEPS for Public Health Practitioners: Strategies and example actions that can improve medication adherence
- CIRCL-Chicago Blood Pressure Measurement Protocol: A 6-step guide for measuring blood pressure
- Improving hypertension surveillance from a data management prospective: Data requirements for implementation of population-based registry: Article describing a study that provides infrastructure for active tracing and monitoring of individuals with HTN
- Million Hearts Hypertension Control Change Package: Process improvements that outpatient clinical settings can implement for optimal hypertension control
- U.S. Blood Pressure Validated Device Listing (VDL): The American Medical Association convened experts to develop VDL Criteria to determine which automated blood pressure (BP) measurement devices have been validated for clinical accuracy
- Visit Checklist -- Supporting Your Patients with High Blood Pressure
Study Results
Results of the CIRCL-Chicago research study are published in scientific journals and in other formats. We are also sharing the results here:
- Carroll AJ, Mohanty N, Lazar D, et al. Establishment of a multi-sector partnership to implement a multilevel intervention for blood pressure control among African Americans on the South Side of Chicago. Conference on the Science of Dissemination and Implementation in Health. 2023.
- Smith JD, Davis P, Kho AN. Community-Driven Health Solutions on Chicago's South Side. Staff Soc Innov Rev. 2021 Summer;19(3):A27-A29. doi: 10.48558/85p7-3113.
- View a Northwestern Institute for Public Health and Medicine (IPHAM) seminar, "Implementation Science & Informatics to Improve Cardiovascular Care in Primary Care Settings," that includes a description of the early phases of CIRCL-Chicago.
eMERGEThe Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network is a National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)-funded consortium tasked with developing methods and best practices for utilization of the electronic medical record (EMR) as a tool for genomic research.
The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network is a National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)-funded consortium tasked with developing methods and best practices for utilization of the electronic medical record (EMR) as a tool for genomic research. It combines DNA biorepositories with electronic medical record (EMR) systems for large-scale, high-throughput genetic research in support of implementing genomic medicine. eMERGE studies and pilots genomic medicine translation through discovery, implementation, tools, and policy.
As a member of the eMERGE consortium, Abel Kho has developed EHR-based phenotyping methods to enable high-throughput genetic studies.
For more information, visit the eMERGE website.
Collaborators:
Baylor College of Medicine Human Genome Sequencing Center (HGSC)
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP)
Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (CCHMC)
Columbia University
Geisinger Health System
Kaiser Permanente Washington (KPW)/University of Washington (UW)
eMERGE Network Coordinating Center
Group Health Cooperative with the University of Washington and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
Harvard University
Mayo Clinic
Meharry Medical College
Partners Healthcare with Broad Institute
Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC)
I-I-CAPTAINThe I-I-CAPTAIN trial implements and tests patient-facing and clinician-facing nudges for HFrEF medication intensification at five health systems through a randomized, implementation-effectiveness trail.
Guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) for patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) improves quality of life, reduces hospitalizations, and extends survival. However, busy clinicians treating stable patients with chronic diseases often "leave well enough alone." This clinical inertia results in GDMT underuse and frequently does not align with patient health preferences.
The I-I-CAPTAIN (Implementation and Interaction of Clinician and Patient-facing Tools Aiming to Intensify Neurohormonal Medicines for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction) trial will implement and test patient-facing and clinician-facing nudges for HFrEF medication intensification at five health systems around the country through a randomized, implementation-effectiveness trail.
The results of this pragmatic trial will answer broad questions related to decision support for evidence-based care, including whether patient-facing or clinician-facing decision support tools are more effective or if the two approaches are additive or synergistic. Ultimately, the trial aims to identify scalable strategies that promote the equitable uptake of evidence-based therapies.
NM Collaborators:
NM Information Services
External Collaborators:
University of Colorado (Lead Site)
Yale University
University of Utah
Sutter Health
Funding:
Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute
Timeline:
2024-2029
Measurement Science Program Colonoscopy Quality Improvement Sub-ProjectAs part of the Veteran’s Affairs (VA)s Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI), the project aims to improve veteran health by facilitating the rapid implementation of quality colonoscopy practices into routine care.
As part of the Veteran’s Affairs (VA)s Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI), the project aims to improve veteran health by facilitating the rapid implementation of quality colonoscopy practices into routine care. This project will enable VA medical centers to implement the measurement and reporting of quality colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening, with a focus on adenoma detection rate (ADR).
Natural language processing (NLP), which is the field studying human-computer interactions, has already been validated for the measurement of ADR. The next step is to apply structured text mining and NLP to national data on the VINCI platform so that each endoscopist’s and facility’s ADR can be calculated, shared and used.
The project has the potential to affect many VA patients across the country, with 8.76 million veterans served by the biggest healthcare system in the country. Report cards—created using the NLP of procedure and pathology free-text notes in the EHR—will be provided for VA colonoscopists to monitor quality of patient care. The VA will roll out this quality improvement initiative to providers throughout the whole network.
Collaborator:
Salt Lake City Veteran’s Administration
NEXT-D3The Natural Experiments for Translation in Diabetes 3.0 (NEXT-D3) Network examines how the Affordable Care Act expansion of Medicaid will affect diabetes diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes among the newly enrolled.
The Natural Experiments for Translation in Diabetes 3.0 (NEXT-D3) Network is a 5-year research collaboration among six academic centers. It examines how the Affordable Care Act expansion of Medicaid will affect diabetes diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes among the newly enrolled. We will compare differences that arise between some states expanding Medicaid and others choosing not to do so. Data will be combined with detailed, longitudinal electronic health record (EHR) data for a large population of 9 million in four expansion and five non-expansion states.
This cooperative agreement is jointly funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) under CDC Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA) Number: RFA- DP10-002, entitled Natural Experiments and Effectiveness Studies to Identify the Best Policy and System Level Practices to Prevent Diabetes and Its Complications.
The NEXT-D project utilizes the CAPriCORN data repository to create the study population. The study population’s individual addresses will then be geocoded to create the control group for analysis. With the connections to CAPriCORN, I.AIM Director Abel Kho is co-principal investigator with another Northwestern University faculty member.
For more information, visit the Next-D website and learn about the Northwestern Site Team.
Collaborators:
Chicago Community Trust
Greater Plains Collaborative
Medical College of Wisconsin
Minnesota Population Center
University of Kansas Medical Center
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)The SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) Project, with funding from an NIH R21 grant, focuses on addressing the need to reduce the time it takes to identify patients with SLE.
The SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) Project, with funding from an NIH R21 grant, focuses on addressing the need to reduce the time it takes to identify patients with SLE. SLE is a difficult to diagnose chronic autoimmune disease affecting more than 200,000 Americans each year. When diagnosed early, SLE treatment can begin sooner and candidates for clinical trials can be identified earlier.
The interdisciplinary project will create a series of algorithms that pinpoint patients with SLE and assess the makeup of the SLE patient population. The team will use electronic health record (EHR) data from multiple health care institutions not only to identify patients, but to cluster similar sub-groups to align these SLE patients with clinical trials and targeted therapy in a timelier fashion.
Co-Principal Investigators:
Theresa Walunas, PhD
Rosalind Ramsey-Goldman, MD, DrPH (Solovy Arthritis Research Society Professor in Rheumatology at Medicine at Northwestern University)
Collaborator:
Abel Kho, MD, MS