Presenting Author:
Principal Investigator:
Lei Liu, Ph.D.
Department:
Preventive Medicine
Keywords:
two-part model; relative abundance; zero-inflated; marginal effect.
Location:
Third Floor, Feinberg Pavilion, Northwestern Memorial Hospital
B169 - Basic Science
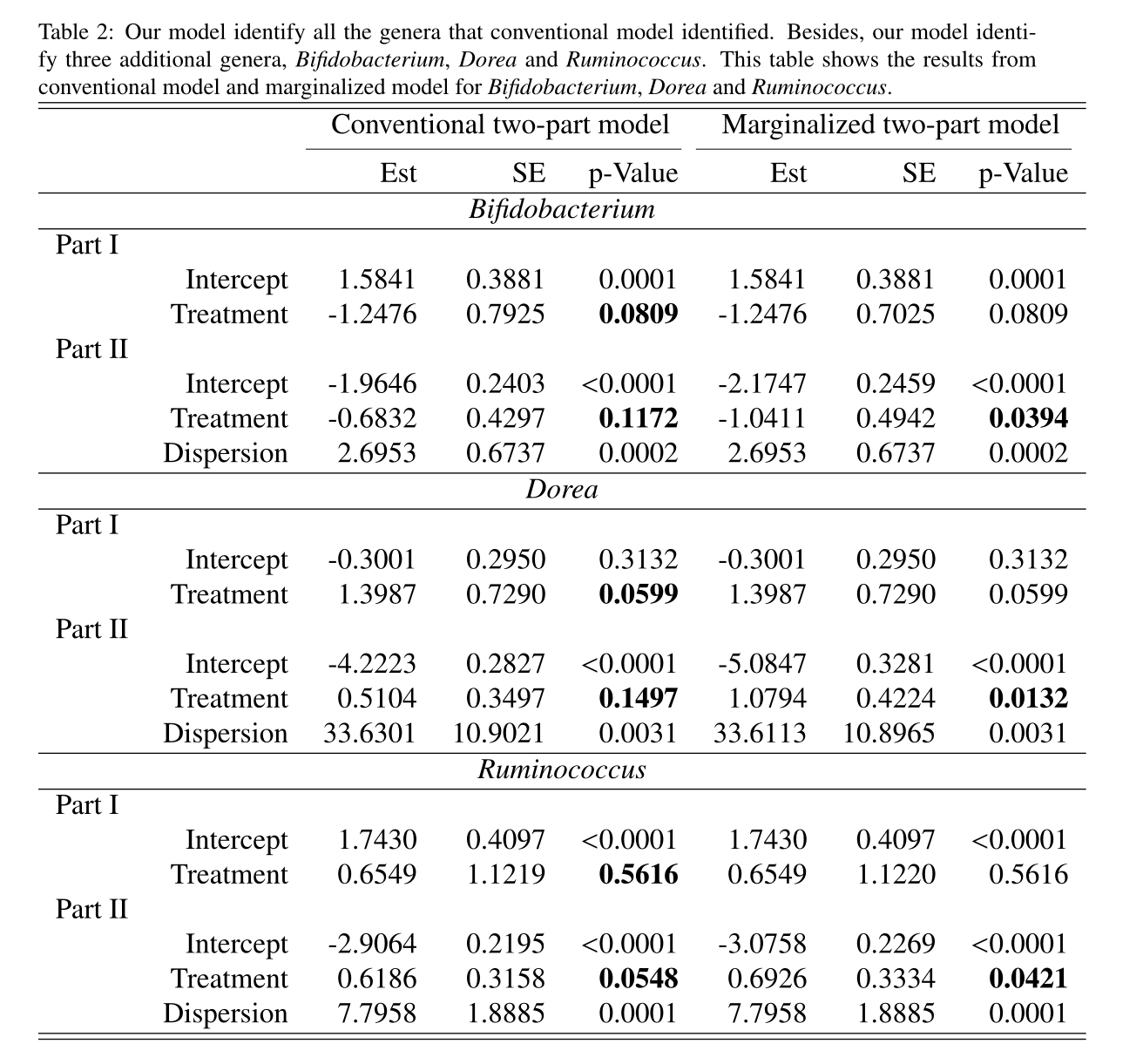
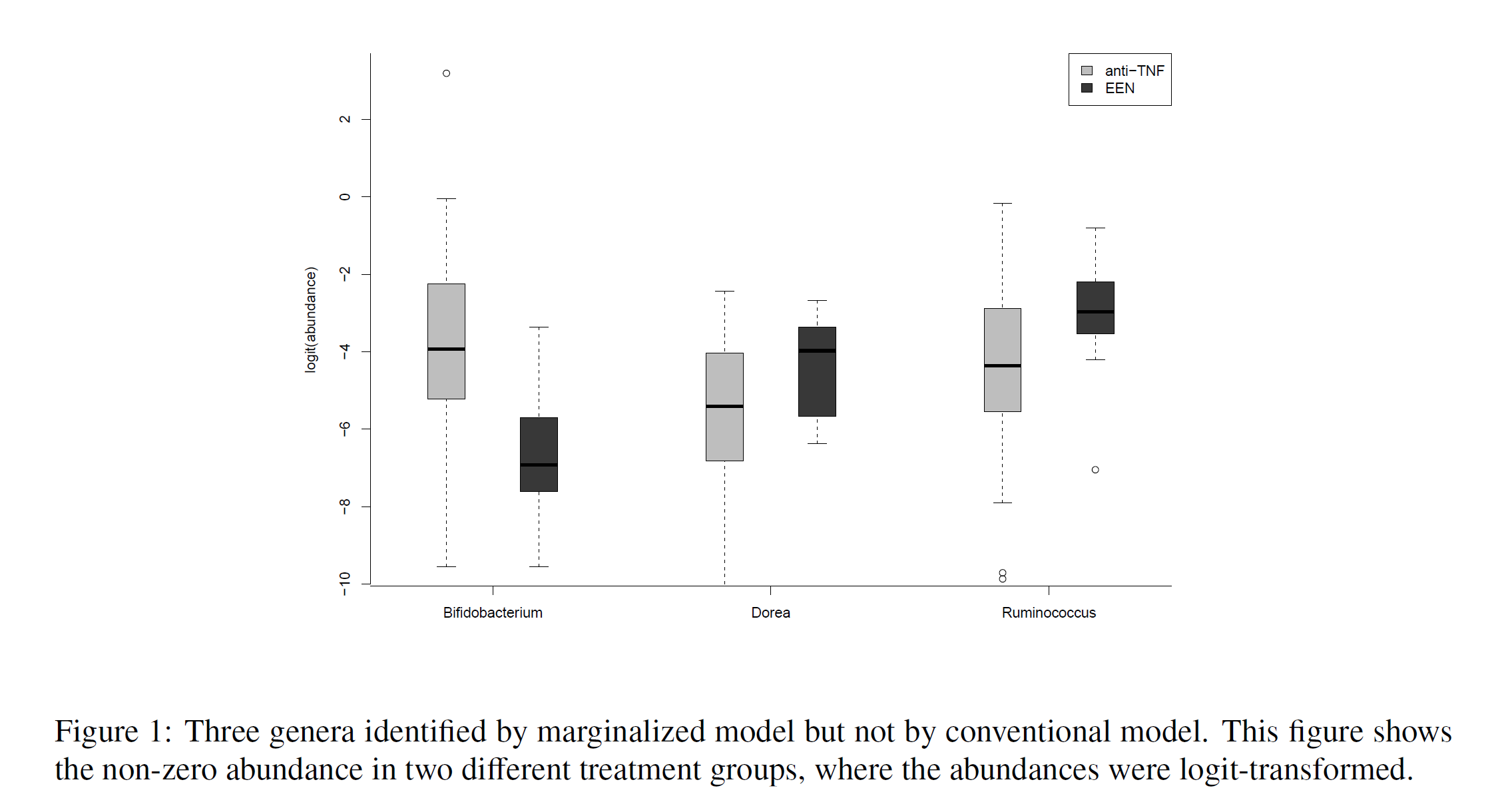
Marginalized Two Part Beta Regression Model for Microbial Compositional Data
Human microbial communities are associated with many human diseases. Microbiome compositional data are highly skewed, bounded in [0, 1), and often sparse with many zeros. A two-part model is commonly used to analyze the “semi-continuous” data. Such two-part model separates zeros and positive values explicitly by two submodels: a logistic model for the probability of microbes being present in Part I, and a Beta regression model for the quantity of relative abundance of microbes in Part II. However, the regression coefficients in Part II cannot provide a marginal interpretation of covariate effects on the microbial abundance. We propose a marginalized two-part Beta regression model which captures the zero-inflation and skewness of microbiome data and also allows investigators to examine covariate effects on the overall marginal mean. Both simulation studies and application to real microbiome data show that our proposed model is a useful tool to examine the marginal effect while accommodating the semi-continuous feature of the microbiome compositional data.